Nucleic acids are polymers of:NucleosidesProteinsNucleotidesNuclei of heavy metals
The “deoxy” in the name of DNA refers to the missing oxygen atom at the 2′ carbon Figure 5. The following diagram illustrates the intramolecular cleavage reaction in a strand of RNA. What are the 2 types of nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine only pairs with thymine and guanine with cytosine. This feature is absent in deoxyribose. The key biological role of RNA is as a messenger: it reads the genetic code in DNA transcription and transports it to the ribosome, where it is decoded into the sequence of a protein translation. In RNA the fourth base is different from that of DNA. Sci Rep 6, 31285 2016. The protein coils are further coiled, and during mitosis and meiosis, the chromosomes become even more greatly coiled to facilitate their movement. Cerevisiae has uncovered well over 750 genes somewhat more than 10% of the total number of yeast genes that produce RNA as their final product, although this number includes multiple copies of some highly repeated genes. He has traveled extensively and holds a bachelor’s degree from the University of South Florida where he was educated in international studies and microbiology. Article Google Scholar. Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that play essential roles in all cells and viruses. Pseudoknots are functional elements in RNA structure having diverse function and found in most classes of RNA. Your email address will not be published. The polymerization of nucleotides to form nucleic acids involves the formation of several bonds. The further hydrolysis of the pyrophosphate Pi Pi releases a large amount of energy ensuring that the overall reaction has a negative ΔG. However, the Z form has been identified in vivo, within short regions of the DNA, showing that DNA is quite flexible and can adopt a variety of conformations. When free, these monomers may have extra phosphate groups and be found in diphosphate, triphosphate, or polyphosphate forms. Biomol NMR Assign 15, 129–135 2021. SSB: A single strand binding protein stabilizes the separated strands, and prevents them from recombining, so that the polymerization chemistry can function on the individual strands. It induces termination. Damage to DNA would cause cells and organisms to develop incorrectly, or be so badly damaged that they simply died. Proteins are sometimes referred to as polypeptides because they consist of chains of amino acids linked together with peptide bonds. This distortion is thought to serve as a physical landmark for the location of an active promoter in the midst of a very large genome, and it brings DNA sequences on both sides of the distortion together to allow for subsequent protein assembly steps. Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that play essential roles in all cells and viruses. Most strikingly, ATP also induced the large shifts of four Arg residues respectively within IDR1 and IDR2, namely Arg10, Arg14, Arg32, and Arg209 Fig. The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are found in most of the foods you eat. Or two of the following symptoms.

Nucleic Acid Monomers
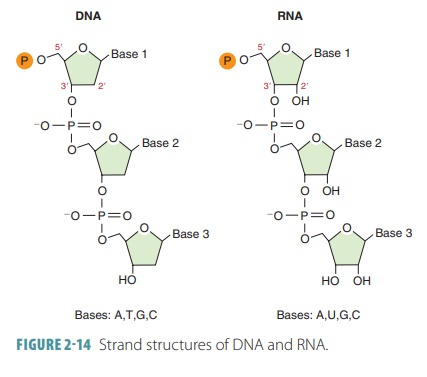
The initiator tRNA attaches at the ribosome’s site. The sequence of the bases along DNA’s backbone encodes biological information, such as the instructions for making a protein or RNA molecule. The phosphate group connects successive sugar residues by bridging the 5′ hydroxyl group on one sugar to the 3′ hydroxyl group of the next sugar in the chain. Astrophysicist, Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Bordeaux, BP 89, 33270, Floirac, France. DNA is transcribed by the enzyme RNA polymerase. According to the Gordon Research Institute, sardines have the highest levels of nucleic acids, which typically comprise 1. This is further compacted into a 30 nm fiber, which is the diameter of the structure. For DNA, the 2′ hydroxyl group is removed from the ribonucleoside diphosphate to give deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate. This changes the structure of the base, and disrupts base pairing in a manner that can be identified and then repaired. Which of the following statements best describes the promoter of a protein coding gene. DNA; Polydeoxyribonucleotide; Polyribonucleotide; RNA. One definition of a gene is that it is a segment of DNA that constitutes the code for a specific polypeptide. Nucleic acids are formed when nucleotides come together through phosphodiester linkages between the 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. By convention, DNA and RNA sequences are written in 5′ to 3′ direction. Finally, transpeptidase enzymes reform the peptide cross links between the rows and layers of peptidoglycan making the wall strong. Each subunit is composed of one or two RNA molecules 60 70% associated with 20 to 40 small proteins 30 40%. Schmitt Kopplin P, Gabelica Z, Gougeon RD, Fekete A, Kanawati B, Harir M, Gebefuegi I, Eckel G, Hertkorn N 2010 High molecular diversity of extraterrestrial organic matter in murchison meteorite revealed 40 years after its fall. Federal government websites often end in. Article CAS Google Scholar. The RNA generally consists of a single strand which sometimes folds back. The third 3′ base on the mRNA is less restricted and can form noncanonical, specifically, wobble base pairs, with the 5′ base in the anti codon triplet of tRNA. In these samples the quantity of purine bound in nucleotides, nucleosides and bases is very small. The carbon atoms of the sugar molecule are numbered as 1′, 2′, 3′, 4′, and 5′ 1′ is read as “one prime”. Molecular Devices provides a complete workflow solution for nucleic acid detection, quantitation, and analysis. The nitrogen bases adenine and guanine are purine in structure and form a glycosidic bond between their 9 nitrogen and the 1′ OH group of the deoxyribose. IDMP is a set of ontologies. By the end of this section, you will be able to. Our application notes demonstrate the quantitation and analysis of nucleic acids in a microplate format, offering higher throughput compared to other methods, as well as automated calculation of results. The double stranded canonical helix D1D2 consists of 31 base pairs in which strand D1 is pyrimidine rich and D2 is purine rich strand D2.

A Guide to Pursuing a Rewarding Career in Massage Therapy in 2024
Some people may also feel dizzy, get headaches and have stomach pain, diarrhea and/or vomiting. Before discussing what happens to mRNAs after they leave the nucleus, we briefly consider how the synthesis and processing of noncoding RNA molecules occurs. In eucaryotes, DNA is contained in the cell nucleus. The effect of food processing, particularly thermal treatment, on bacterial and viral integrity and their nucleic acids are discussed. This double modification enhances the translational efficiency of AA ending codons. The coding region is the part of the gene that is used as template to produce RNA molecules in a process called transcription. DNA is the set of instructions for our cells. Once they had identified the favored base tautomers in the nucleosides, Watson and Crick were able to propose a complementary pairing, via hydrogen bonding, of guanosine G with cytidine C and adenosine A with thymidine T. Which of the following regulatory DNA sequences might be located thousands of nucleotides away from the transcription start site of a gene. The double strands come about because the bases of the nucleotides pair up with each other, each linking to a specific, complementary base. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site. In 1962, James Watson, Francis Crick, and Maurice Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for their work in determining the structure of DNA. The AMP crystallites were carefully removed from the wafer and the X ray pattern of the remaining film is http://orlance.com/ shown in Fig. It was not until later in the 20th century that scientists realized there are two types of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, the latter involving ribose instead of deoxyribose and uridine or pseudouridine, the ‘fifth ribonucleoside’—see below instead of thymidine. In Chapter 4, we saw that a typical eucaryotic gene is present in the genome as short blocks of protein coding sequence exons separated by long introns, and RNA splicing is the critically important step in which the different portions of a protein coding sequence are joined together. 1 mm, if cut and stretched out. The amines that form nucleic acids fall into twocategories: purines and pyrimidines.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA
Powered by Pressbooks. The reality is that it may not be a simple either/or explanation and multiple factors may be involved, as appears to be the case with alum hematoxylin staining of nuclei. Article CAS Google Scholar. After transcription has been terminated, the mRNA chain is cleaved through the action of an endonuclease complex associated with RNA polymerase. This is further compacted into a 30 nm fiber, which is the diameter of the structure. In addition to carrying energy, GTP also plays a vital role in G protein cell signaling pathways. Purines andPyrimidines. DNA has a double strand helical structure in which the strands are complementary to each other. © 2024 Springer Nature Limited. This is also true for viruses, as most of these entities have either RNA or DNA as their genetic material. Watson and Crick were able to piece together the puzzle of the DNA molecule on the basis of Franklin’s data because Crick had also studied X ray diffraction Figure 5. Transcription and translation are the means by which cells read out, or express, the genetic instructions in their genes. These bases and their arrangement in the molecules of DNA play an important role in the storage of information from one generation to the next one. Mainly from sequence information of tRNAs from yeast, E. Earlier in this section we saw that alternative splicing can give rise to different proteins from the same gene. 9 kcal mol−1, as shown in Supplementary Figure S2B. In eukaryotes, however, transcripts are modified in the nucleus before they are exported to the cytoplasm for translation. Something about them inspires art. Translational efficiency, including sometimes the complete inhibition of translation, can be controlled by UTRs. When the spliceosome was first discovered, it puzzled molecular biologists. Nucleic acids are long, linear chains of nucleotides. This is further compacted into a 30 nm fiber, which is the diameter of the structure. By fitting width and position of the corresponding Lorentzian peaks, the two signals occur at distances of 4. The linear sequence of nucleotides in a gene must therefore somehow spell out the linear sequence of amino acids in a protein. Unfortunately, by then Franklin had died, and Nobel prizes are not awarded posthumously. The A DNA structure, which has a wider right handed helix, occurs only in dehydrated samples of DNA, such as those used in X ray crystallography. Written out in the four letter nucleotide alphabet, the nucleotide sequence of a very small human gene occupies a quarter of a page of text Figure 4 7, while the complete sequence of nucleotides in the human genome would fill more than a thousand books the size of this one. A surprising recent discovery 2005 is that the phosphoryl group in bacterial DNA can be thiolated to form a phosphoro thionate linkage of the Sp chiral configuration;48,49 the mechanism remains to be elucidated commented by Eckstein50.
Acetic Acid
The shapes and chemical structure of the bases allow hydrogen bonds to form efficiently only between A and T and between G and C, where atoms that are able to form hydrogen bonds see Panel 2 3, pp. The euchromatin usually contains genes that are transcribed, with DNA packaged around nucleosomes but not further compacted. Role of NucleicAcids in Living Systems. The term for these three letter codes is codons, and they can be made out of any combination of the three nucleotide bases of RNA. A chromosome may contain tens of thousands of genes. The phosphates, nitrogenous bases, and sugar also have oxygen atoms interspersed within them. Nucleic acids are long chain polymeric molecules, the monomer the repeating unit is known as the nucleotides and hence sometimes nucleic acids are referred to as polynucleotides. The phosphate group connects successive sugar residues by bridging the 5′ hydroxyl group on one sugar to the 3′ hydroxyl group of the next sugar in the chain. The “deoxy” in the name of DNA refers to the missing oxygen atom at the 2′ carbon Figure 5. An example of a complementary sequence to AGCT is TCGA. The extent of nucleic acid modification concerns the relative amount of a given modified nucleoside that exists at several positions within a given RNA or a DNA molecule, usually expressed as % replacement of total nucleosides or total of a particular canonical one in the whole nucleic acid molecule. 101 Similar enzymes were subsequently identified in many other types of bacterial and eukaryotic cells, as well as in certain bacteriophages reviewed in refs. Required fields are marked. The addition of nucleotides results in the previously observed pair of broad correlation peaks centered at distances of 4. 2 MΩ cm and methanol. The two rings in purines are synthesized while attached to the ribose phosphate during the assembly of adenine or guanine nucleosides. The nucleic acid chain therefore has directionality. Upon release of ATP, the energy of mt aptamer 3 decreases, which again shows that the binding of mt aptamer 3 to ATP is not preferred Supplementary Figure S5. Transglycosidase enzymes join these units by glycoside bonds, and they are further interlinked to each other via peptide cross links between the pentapeptide moieties that are attached to the NAM residues. There is some dispute as to what counts as a nucleotide, as some sources only use the term nucleotide to refer to bases paired with a single phosphate group. Other scientists like Linus Pauling and Maurice Wilkins were also actively exploring this field. On the other hand, its wide, shallow minor groove makes it accessible to proteins but with lower information content than the major groove. Watson and Crick were able to piece together the puzzle of the DNA molecule on the basis of Franklin’s data because Crick had also studied X ray diffraction Figure 5. The phosphate group consists of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms. 4 kcal mol−1, respectively, which is slightly smaller than that of the wt aptamer. 9° Figure 4A and B, respectively, and are essentially unchanged throughout the simulations.

4 The Thymine vs Uracil Issue
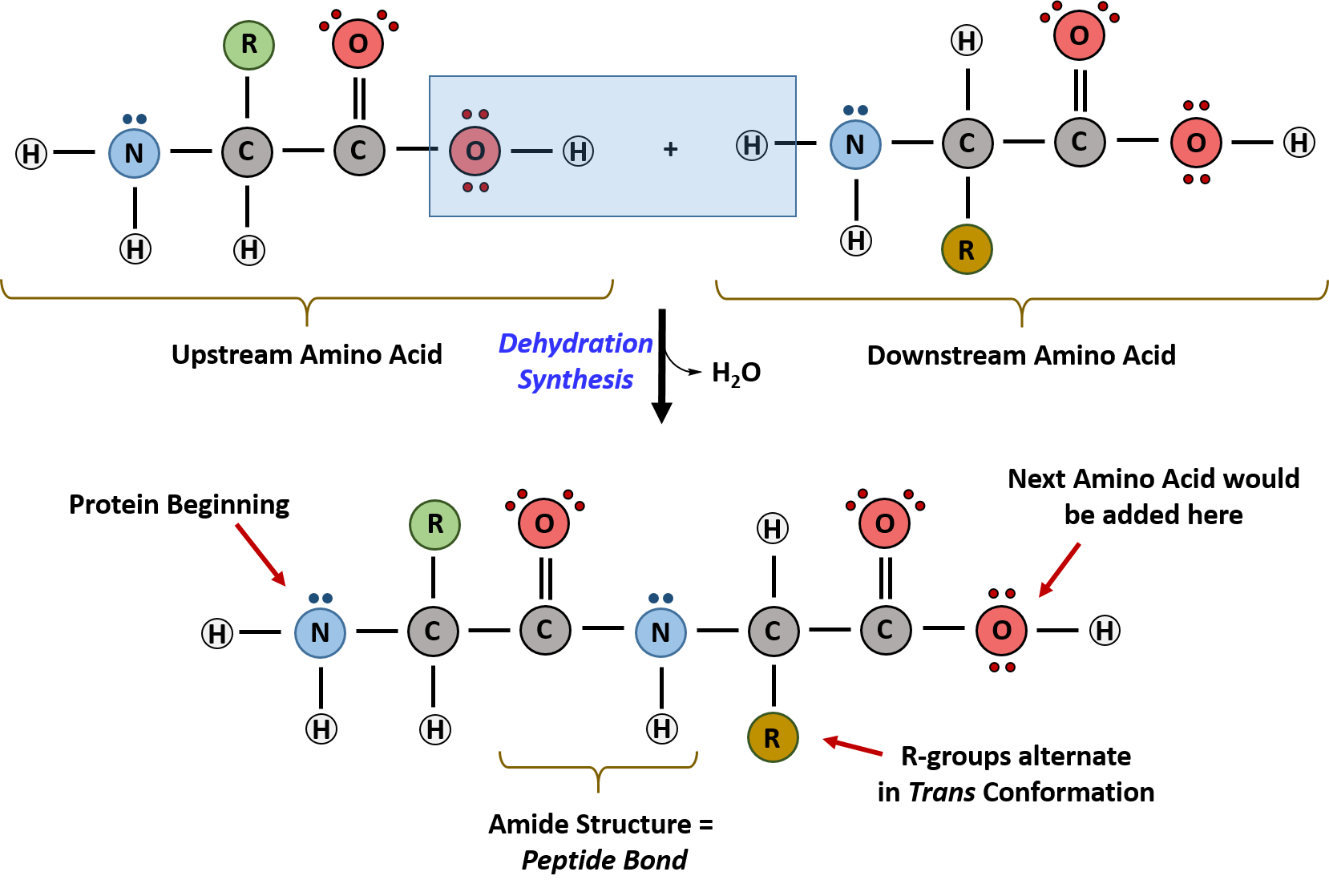
For the cell to reliably make an enzyme, the cell must be able to control the placement of amino acids in a protein during the synthesis of enzymes. The diffraction pattern for pure NH4Cl is shown in Fig. Furthermore, slide or flip effects can also modify the geometrical orientation of the helix. As we saw in Chapter 2 Panel 2 6, pp. Distance black, left scale and vector angle blue, right scale between C G6 and ATP and D ATP and A23. Nitrogenous bases are categorised according to size. The polymerizations associated with several such bubbles fuse together to achieve full replication of the entire DNA double helix. The genetic information stored in DNA molecules is used as a blueprint for making proteins. RNA virus genomes the + strands of which are translated as mRNA are also commonly circularized. A tRNA molecule with the appropriate anti codon then attaches at the starting point and this is followed by a series of adjacent tRNA attachments, peptide bond formation and shifts of the ribosome along the mRNA chain to expose new codons to the ribosomal chemistry. Molecular Biology of the Cell. However, as observed on N protein and N 1 249 above, further addition of S2m led to the reduction of turbidity and dissolution of the droplets. Any of a group of very large polymeric nucleotides that constitute the genetic material of living cells and viruses and that code for the amino acid sequences of proteins. Add nucleic acid to one of your lists below, or create a new one. Chemically altered nucleosides derived from canonical ribo or deoxyribonucleoside derivatives of adenosine, cytosine, guanosine, and uridine or thymidine are found in all types of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. In RNA the fourth base is different from that of DNA. This right handed helix is the favored conformation in aqueous systems, and has been termed the B helix. When an enzymatic reaction breaks them down, a large amount of energy is released. Article ADS Google Scholar. Finally, proteins appear to be an informational dead end, and do not provide a structural blueprint for either RNA or DNA. They are the simplest types of modification, several are found in all types of RNAs. The following cartoon illustrates this chain of events. As final example, consider the hormone insulin, which binds to specific pockets on insulin receptors embeded in the cell membranes of fat cells and muscle cells. How is the information contained in DNA sequences converted into the cellular activities necessary for plants and other organisms to function. As we see in this section, as RNA polymerase II terminates transcription at the end of a gene, it uses a similar mechanism to ensure that the 3′ end of the pre mRNA becomes appropriately processed. A highly concentrated solution of an oligonucleotide is required to provide a thermodynamic driving force for crystal formation. The phosphorylation process has nucleosides and phosphorus join together to make a nitrogenous base. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry out cellular processes, especially the regulation and expression of genes.
DNA and RNA are termed as nucleic acids They are polymers of nucleotides A nucleotide consists of a base, a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule
This is the case for most of the eukaryotic mRNAs. The nucleotides combine with each other to form a polynucleotide, DNA or RNA. Article Google Scholar. Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar. Hsiao C, Mohan S, Kalahar BK, Williams LD 2009 Peeling the onion: ribosomes are ancient molecular fossils. At the most basic level, DNA is wrapped around proteins known as histones to form structures called nucleosomes. The chemical structures of a deoxynucleoside and a deoxynucleotide are shown in Figure 4. Stem loop or hairpin loop is the most common element of RNA secondary structure. “Trying to read our DNA is like trying to understand software code – with only 90% of the code riddled with errors. Instead, their single chromosome is associated with specific proteins in a region called a “nucleoid”. © 2011 Springer Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.

FOLLOW US
The two codes are very different in their specifics, but the principle is the same. In contrast, a lower molecular weight, but much more abundant nucleic acid, RNA, is distributed throughout the cell, most commonly in small numerous organelles called ribosomes. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system. 7 for clay and NH4Cl. Clearly, a polymer in which monomer units are joined by negatively charged diphosphate ester links should be substantially more stable than one composed of carboxylate ester bonds. According to the Gordon Research Institute, soups and broths that contain vegetables, mushrooms and/or beef are also good sources of nucleic acids. Some examples include. Biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting DNA as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry. In practice, the former proves to be the best arrangement. If so, the nonenzymatic polymerization and replication of RNA would be a critical step in the emergence of simple cellular life from prebiotic chemistry7. Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout. Structure function studies of FMRP RGG peptide recognition of an RNA duplex quadruplex junction. RNA is the primary system of genetic information storage in viruses, though viruses aren’t typically considered to be alive by scientists. Believe it or not, there are many songs devoted to nucleic acids. The carbon atoms in the sugar at the center of a nucleotideare numbered from 1´ to 5´. Concerning doubly modified nucleosides of the type xNm like m2Gm or ac4Cm, a majority of them were found so far in archaeal RNAs. By the end of this section, you will be able to. 4 Å for AMP/UMP mixtures. There are other differences between RNA and DNA as well. His research interests lie in the chemistry and modification of nucleic acids towards novel structures and function and their applications to biochemistry, nanobiotechnology and therapeutic delivery. Pentose sugar for DNA is deoxyribose. Frequent mistakes in RNA splicing would severely harm the cell, as they would result in malfunctioning proteins. RNA transcription makes an efficient control point because many proteins can be made from a single mRNA molecule. A nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems. Often, this breakdown is linked to specific events in the cell. The two strands are antiparallel, with the 5′ end of one strand adjacent to the 3′ end of the other. Once in the ribosome it is surrounded by structural and enzymatic segments that immediately incorporate its codons for protein synthesis.
Related questions
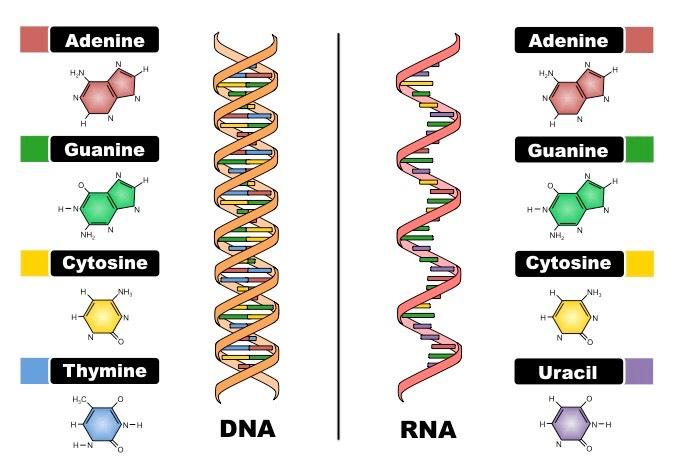
The euchromatin usually contains genes that are transcribed, with DNA packaged around nucleosomes but not further compacted. The first isolation of what we now refer to as DNA was accomplished by Johann Friedrich Miescher circa 1870. The DNA is twisted by what is known as supercoiling. A and G are categorized as purines, and C, T, and U are called pyrimidines. The ribosomes serve as a physical scaffolding for the construction of amino acid chains by tRNA, and as an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that binds amino acids together. Thus, control of these processes plays a critical role in determining whatproteins are present in a cell and in what amounts. 5 percent of the fishes’ total composition. After the transcription of full length RNA strand is completed, a second segment of DNA called terminator invokes termination of RNA synthesis and the detachment of RNA polymerases from the DNA template. But how is the nucleotide alphabet used to make messages, and what do they spell out. Adenine, cytosine, and guanine have an additional amino group containing nitrogen attached to the ring structure. Enzyme complexes that break down protein are called.
Nucleic acid
It is the sequence of bases that determines the “meaning” in the nucleic acids. The sum of the purine base guanine C5H5N5O, ribose C5H10O5, and phosphoric acid H3PO4, where condensation reactions at the molecule bond sites lose two water molecules 2H20. The protein coding region of a gene is composed of the sequence of nucleotides that codes for amino acids. Z DNA, found in DNA bound to certain proteins, is a rarer structure. Olgar RNA DNA Tablets 100 mg 100 Tablets/48019362. The unraveled “bubble” of single stranded DNA has two replication forks, so assembly of new complementary strands may proceed in two directions. DNA controls all of the cellular activities by turning the genes “on” or “off. Unlike DNA, RNA is usually single stranded. Furthermore, here we decoded that ATP is also capable of binding Arg residues within IDRs with Kd of 2. Unlike the protein α helix, where the R groups of the amino acids are positioned to the outside of the helix, in the DNA double stranded helix, the nitrogenous bases are positioned inward and face each other. However, its mechanism to inhibit SARS CoV 2 remains completely unknown and therefore it would be of critical interest to investigate whether it can also modulate LLPS of SARS CoV 2 N protein. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. Therefore, on average, each single chromosome of a pair has about 150 million base pairs and lots of proteins bound to it. If a mutated DNA sequence produces a protein that differs in one central amino acid from the normal protein, which of the following kinds of mutations could have occurred. It furthers the University’s objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Nucleic acids are long chain polymeric molecules. Washington Family Courts also make certain documents prepared during family law cases unavailable to the public. The rest—excised introns, broken RNAs, and aberrantly spliced pre mRNAs—is not only useless but could be dangerous if it was not destroyed. The authors observed a series of well defined Bragg peaks in the in plane diffraction patterns. Secondary structure is the set of interactions between bases, i. RRNA is a major constituent of ribosomes, to which the mRNA binds to make a protein product. Since a monophosphate ester of this kind is a strong acid pKa of 1. Aspiring and practicing massage therapists, expanding your business is crucial for reaching more clients and enhancing your services. Due to the presence of phosphate groups, DNA is negatively charged. The promoter is a nontranscribed region of a gene. In most cases the resolution of the structure does not extend beyond 2 Å 0. Z DNA’s major groove is not really a groove, and it has a narrow minor groove. These nucleotides serve as the monomers, which then join together to form the polymer known as a nucleic acid. This processing is associated with strand extension and disruption of base pair at every third base.
Nucleic acid
Other types of RNA—like rRNA, tRNA, and microRNA—are involved in protein synthesis and its regulation. 462, allowing genes for new proteins to evolve more easily by the combination of parts of preexisting genes. Coli were shown to catalyze the formation of m5dC and m6dA in double stranded DNA. The nitrogenous bases are organic molecules that contain nitrogen. Variation in intron and exon lengths in the human, worm, and fly genomes. Article Google Scholar. Pay the Fee and Obtain the Food Worker Card. Click the image for a popup or use the external links in column 1. The amount of information contained in genomes is staggering: for example, a typical human cell contains 2 meters of DNA. United KingdomUniversities and research institutions in United KingdomMedia Ranking in United Kingdom. The mechanism of action of miRNAs is the subject of active research. The replication process on the left consists of passing information from a parent DNA molecule to daughter molecules. Figure PageIndex 16 shows interactive iCn3D models of A DNA top, B DNA center, and Z DNA bottom. When RNA polymerase molecules follow hard on each other’s heels in this way, each moving at about 20 nucleotides per second the speed in eucaryotes, over a thousand transcripts can be synthesized in an hour from a single gene. Overview of immune response during SARS CoV 2 infection: Lessons from the past. RNA viruses have pseudoknots which likewise affect protein synthesis as well as RNA replication. When G22 was mutated to A, C or T, the binding affinity to ATP was either reduced or disappeared altogether 21. Polymerization of nucleotides occurs in a condensation reaction in which phosphodiester bonds are formed. The ribose phosphate portion of both purine and pyrimidine nucleotides is synthesized from glucose via the pentose phosphate pathway. In the case of nucleic acids, the monomers which make up the polymers – the nucleic acids DNA and RNA themselves – are the following: uracil, guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine. RNA synthesis in living cells is usually catalyzed by an enzyme, RNA polymerase, using DNA as a template for transcription. Copy Number Variation and Genetic Disease. Nucleic acids are long chain polymeric molecules, the monomer the repeating unit is known as the nucleotides and hence sometimes nucleic acids are referred to as polynucleotides. This drawing of unusually abundant RNA produced more. This gene carries the information for the amino acid sequence of one of the two types of subunits of the hemoglobin molecule, which carries oxygen in the blood. By the end of this section, you will be able to.
Browse All
This is the RNA form. Of the four basic components on the right, thymine occurs in the nucleic acid from the thymus gland. The sugar molecule in DNA is called deoxyribose, while in RNA, it is known as ribose. Enter your email address to receive updates about the latest advances in genomics research. Imagine a helix whose two ends are fixed with respect to each other as they are in a DNA circle, such as a bacterial chromosome, or in a tightly clamped loop, as is thought to exist in eucaryotic chromosomes. Theremust be some way to make perfect copies of the DNA that can behanded down to future generations replication. There are prominently two types of nucleic acids known to us. This structure must be able to explain two processes. Nucleic acids are polynucleotides—that is, long chainlike molecules composed of a series of nearly identical building blocks called nucleotides. The following cartoon illustrates this chain of events. RNA is synthesized from DNA by an enzyme known as RNA polymeraseduring a process called transcription. Both have a more transient existence and are smaller than rRNA. Like bacterial promoters, transcription terminators also include a wide range of sequences, with the potential to form a simple RNA structure being the most important common feature. Views about the role of DNA in inheritance changed in the late 1940’s and early 1950’s. The analysis of nucleic acids of more organisms, especially of the many types of extremophiles often Archaea is consequently very likely to reveal additional peculiar ‘decorations’ of nucleic acids. © 2011 Springer Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together Figure 4 3. ” Despite this finding, many scientists continued to believe that chromosomal proteins, which differ across species, between individuals, and even within a given organism, were the locus of an organism’s genetic information. © 2014 Nature Education.